Download all my infographics about the tenses in PDF here.
Download all my explanations of the tenses in PDF here.
What's The Difference?
- How to choose: Future with 'will' or future with 'be going to'?
- How to choose: Present Perfect or Past Simple?
- How to choose: Present Simple or Present Continuous?
- How to choose: Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous?
- Tenses Cheatsheet
- Grammar Exercises
- Present Simple Spelling Changes
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Irregular Verbs, Lists and Exercises
- How to pronounce 'ed'
- Stative verbs
This is a printable PDF of all the verb tenses and how to form them.
This is a list of all the grammar exercises on this site, about verb tenses and other things.
This is an explanation of how we sometimes need to change the spelling of a verb with 'he, she, it' in the present simple, for example why 'cry' becomes 'cries' but 'play' is 'plays'.
Adverbs of Frequency are words like 'often' 'sometimes' 'never'. This page shows you how to use them with the present tense and where to put them in the sentence. I also explain about longer phrases like 'from time to time'.
How do you pronounce 'stopped'? Many students say 'stop-id' instead of 'stopt'. This page explains the rules of pronunciation for regular past simple verbs and past participles (verbs that end with 'ed')
We can't use some verbs, like 'know' or 'believe' in continuous tenses. This page has lists and explanations.
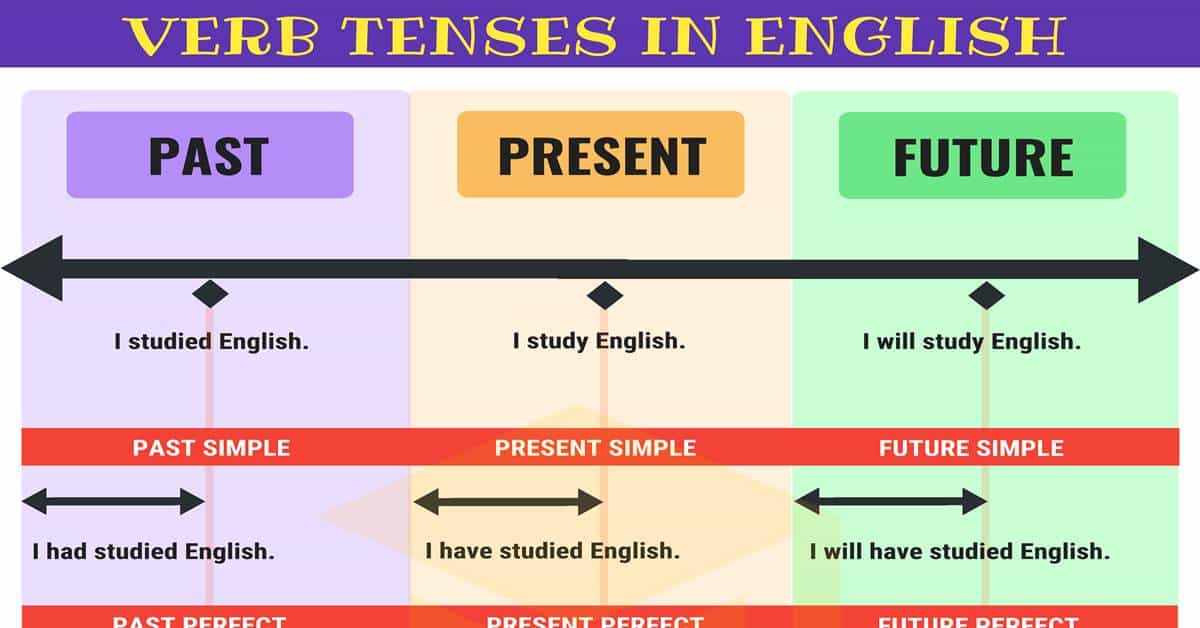
Verb Tenses
Verbs come in three tenses: past, present, and future. The past is used to describe things that have already happened (e.g., earlier in the day, yesterday, last week, three years ago). The present tense is used to describe things that are happening right now, or things that are continuous. The future tense describes things that have yet to happen (e.g., later, tomorrow, next week, next year, three years from now).
The following table illustrates the proper use of verb tenses:
| Simple Present | Simple Past | Simple Future |
| I read nearly every day. | Last night, I read an entire novel. | I will read as much as I can this year. |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous | Future Continuous |
| I am reading Shakespeare at the moment. | I was reading Edgar Allan Poe last night. | I will be reading Nathaniel Hawthorne soon. |
| Present Perfect | Past Perfect | Future Perfect |
| I have read so many books I can’t keep count. | I had read at least 100 books by the time I was twelve. | I will have read at least 500 books by the end of the year. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | Future Perfect Continuous |
| I have been reading since I was four years old. | I had been reading for at least a year before my sister learned to read. | I will have been reading for at least two hours before dinner tonight. |
No comments:
Post a Comment